-
(+91) 9136069390
Please feel free to contact our friendly reception staff with any general or medical enquiry.
Make Appointment - Call Us: (+91) 9136069390
- drrajeshgaekwad@gmail.com
- Mon to Sat: 9:00 AM - 10:00 PM
Treatments
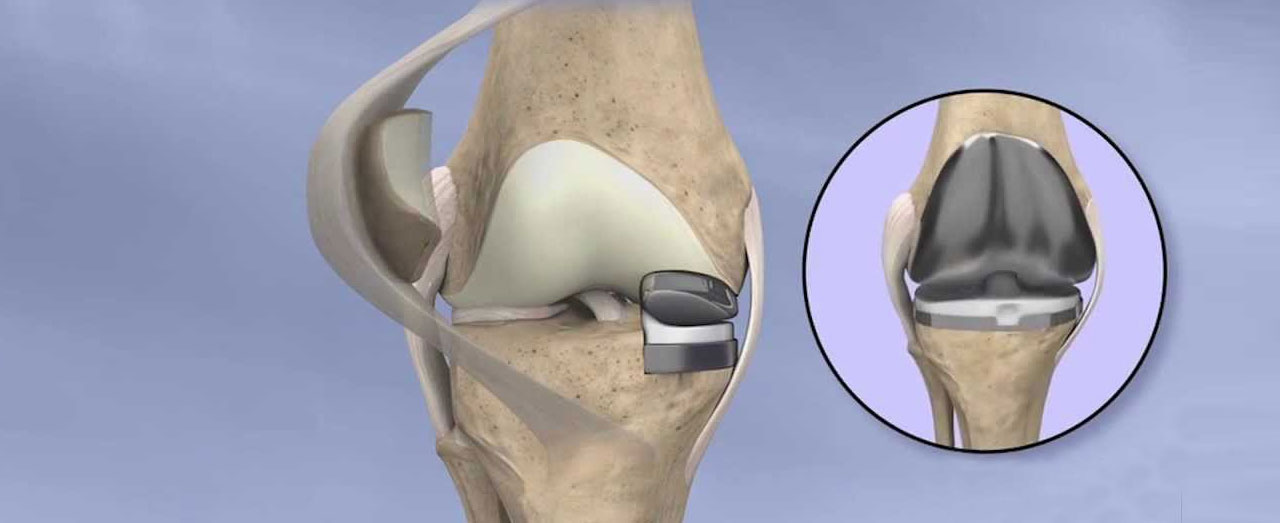
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA), is a surgical procedure that replaces only the damaged part of the knee joint, preserving the healthy areas. This surgery is typically recommended for patients with osteoarthritis confined to a single compartment of the knee, either the medial (inner), lateral (outer), or patellofemoral (front) compartment.
Indications for Partial Knee Replacement
- Unicompartmental Osteoarthritis: Arthritis limited to one compartment of the knee.
- Minimal Deformity: No significant knee deformity (such as severe bow leg or knock knee).
- Intact Ligaments: Cruciate ligaments (ACL and PCL) are intact and functional.
- Moderate Activity Level: Suitable for patients with a lower demand for high-impact activities.
Advantages of Partial Knee Replacement
- Less Invasive: Smaller incision and less bone removal compared to total knee replacement.
- Faster Recovery: Shorter hospital stay and quicker return to normal activities.
- Less Pain Postoperatively: Reduced pain and swelling after surgery.
- Natural Knee Movement: Better preservation of natural knee kinematics due to retention of healthy bone, cartilage, and ligaments.
- Reduced Blood Loss: Less intraoperative blood loss.
Components of a Partial Knee Replacement
- Femoral Component: Replaces the damaged end of the thigh bone (femur).
- Tibial Component: Replaces the top of the shin bone (tibia).
- Polyethylene Insert: A plastic insert that fits between the metal components to facilitate smooth movement.
Risks and Complications
- Infection: At the surgical site or deep within the joint.
- Blood Clots: In the legs or lungs.
- Implant Problems: Loosening, wear, or mechanical failure of the components.
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: Injury during surgery.
- Stiffness or Loss of Motion: Reduced knee flexibility.
- Disease Progression: Arthritis may progress to other compartments of the knee, potentially requiring total knee replacement in the future.



