-
(+91) 9136069390
Please feel free to contact our friendly reception staff with any general or medical enquiry.
Make Appointment - Call Us: (+91) 9136069390
- drrajeshgaekwad@gmail.com
- Mon to Sat: 9:00 AM - 10:00 PM
Treatments
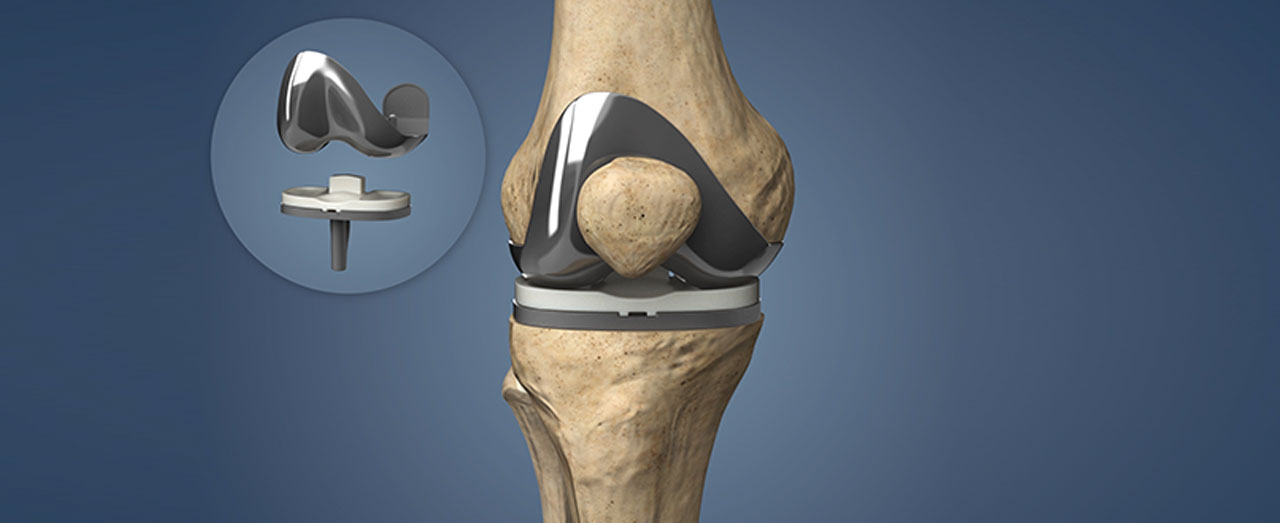
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement (TKR), also known as total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace a damaged or diseased knee joint with artificial components. This surgery is typically performed to relieve pain and restore function in patients with severe knee arthritis or other significant knee joint damage.
Indications for Total Knee Replacement
- Osteoarthritis: Severe wear-and-tear arthritis causing pain, stiffness, and loss of function.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Chronic inflammatory arthritis affecting the knee.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis following a knee injury.
- Knee Deformities: Conditions like bow legs or knock knees.
- Failed Previous Knee Surgery: When prior knee surgeries have not provided adequate relief.
Components of a Total Knee Replacement
- Femoral Component: Replaces the end of the thigh bone (femur).
- Tibial Component: Replaces the top of the shin bone (tibia).
- Patellar Component: May replace the underside of the kneecap (patella).
- Polyethylene Spacer: A plastic insert that fits between the metal components to facilitate smooth movement.
Risks and Complications
- Infection: At the surgical site or deep within the joint.
- Blood Clots: In the legs or lungs.
- Implant Problems: Loosening, wear, or mechanical failure of the components.
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: Injury during surgery.
- Stiffness or Loss of Motion: Reduced knee flexibility.
- Allergic Reactions: To the materials in the implants.
Advantages of Total Knee Replacement
- Pain Relief: Significant reduction or elimination of knee pain.
- Improved Mobility: Enhanced ability to perform daily activities.
- High Success Rate: Most patients achieve excellent outcomes.
- Durable Results: Long-lasting improvement in joint function.



